Vr Mapping |
ON-LINE REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION CARDINAL SYSTEMS, LLC |
Insert Catenary (InsCat)
Type: Semi-automatic interactive application
Detailed Description
Power lines are typically represented as catenaries. A catenary is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends. The curve has a U-like shape and mathematically, the curve is the graph of the hyperbolic cosine function.
Semi-automatic delineation of power lines and other isolated linear features given a single user specified start point. The line terminates at peaks or obstructions (insulators, poles, etc.) in an attempt to isolate wire attach points at the end points of the catenaries. The algorithm is reasonably robust to sparse data. Quality control tools allow fast viewing and editing of line terminations.
Insert Catenary is designed to work with LiDAR and point cloud data. This application may be started from a Function Key.
Please see also Catenary to POA (Point of Attachment)
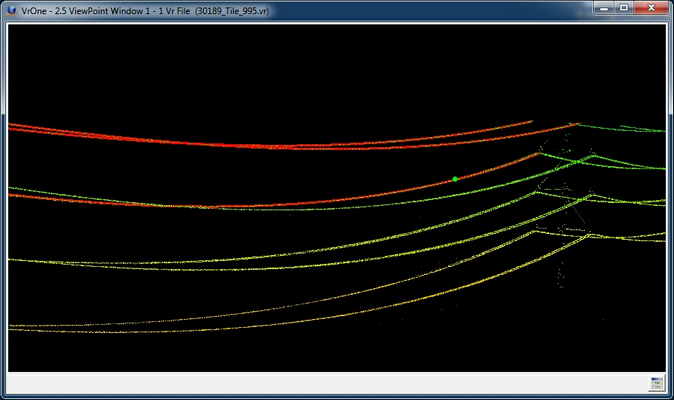
Power line catenaries
Button Assignments
Insert Catenary – Main
When Insert Catenary starts, an initial point or points along the catenary needs to be digitized. This initial data provides seed information so the application can follow the catenary and place a 3D line.
Main Menu
|
Button |
Description |
1 |
Initial point |
Identifies one, two or three points along a catenary to provide initial data to start the catenary line insertion |
2 |
||
3 |
Review line |
Review an existing line |
4 |
Extend/hack |
Extend or hack an existing line |
5 |
Join lines |
Joins two existing lines using a user defined join point |
6 |
|
|
7 |
Enter params |
Enter/edit Insert Catenary parameters (see Insert Catenary Parameters) |
8 |
Del last line |
Deletes the last saved line |
9 |
Del line |
Deletes a line by identifying an existing line |
* |
|
|
0 |
|
|
# |
End |
Ends application |
Insert Catenary – Review
Review drives the cursor along an existing, user identified line.
Review Menu
|
Button |
Description |
1 |
||
2 |
Next point |
Moves cursor to the next line point |
3 |
Prev point |
Moves cursor to the previous line point |
4 |
First point |
Moves cursor to the first point on the line |
5 |
Last point |
Moves cursor to the last point on the line |
6 |
|
|
7 |
||
8 |
||
9 |
||
* |
|
|
0 |
|
|
# |
End |
Ends review and returns to the main menu |
Insert Catenary – Extend/hack Line
The cursor may be placed near an existing line and the closest line will be extended to or hacked at the point digitized (the hack point). If the line is to be extended the endpoint on the line will be extended along the azimuth of the last line segment. If the line is to be hacked the shortest side of the line will be hacked at a 90 degree offset from the hack point. After the hack point has been digitized and the line extended or hacked, the result may will be displayed and may be accepted or rejected before re-saving the line.
Extend/hack Menu
|
Button |
Description |
1 |
Id hack line |
Identifies line to be extended/hacked |
2 |
||
3 |
||
4 |
||
5 |
||
6 |
|
|
7 |
||
8 |
||
9 |
||
* |
|
|
0 |
|
|
# |
End |
Ends Extend/hack and returns to the main menu |
After the line to be extended or hacked is identified a hack or extend point is digitized and the result may be accepted or rejected.
Insert Catenary – Join Lines
Two existing lines may be joined by placing the cursor near both lines and digitizing a point (the join point). The join point will be the common point between the two lines. Lines will be extended or hacked to the join point. After the join point has been digitized and the lines joined, the result may will be displayed and may be accepted or rejected before re-saving the lines.
Join Lines Menu
|
Button |
Description |
1 |
Id join line N |
Identifies the two lines to be joined |
2 |
||
3 |
||
4 |
||
5 |
||
6 |
|
|
7 |
||
8 |
||
9 |
||
* |
|
|
0 |
|
|
# |
End |
Ends Join Lines and returns to the main menu |
After the two lines to be joined are identified a join point is digitized and the results of the join may be accepted or rejected.
Insert Catenary – Delete Line
Deletes an existing line. When a line is identified to be deleted it may be accepted or rejected before deletion.
Delete Line Menu
|
Button |
Description |
1 |
Id line |
Identifies the line to delete |
2 |
||
3 |
||
4 |
||
5 |
||
6 |
|
|
7 |
||
8 |
||
9 |
||
* |
|
|
0 |
|
|
# |
End |
Ends Delete Line and returns to the main menu |
Insert Catenary Parameters
The Insert Catenary parameters may be defined by pressing button 7 from the Main menu.
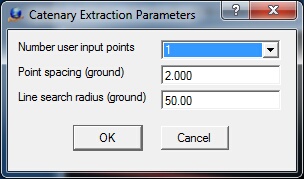
Parameters
Number user input points
Defines the number of user digitized points to use to provide initial data to starts the catenary line insertion. Catenary input given a single user input point is the default option. However, the adaptive methods used to determine the direction, radius and point spacing along the curve can fail. Failure is more probable in sparse data and closely space wires. In the event of failure switch to multiple input points.
When using two input points they are used to identify a linear section of the curve and hence should not be too far apart. When using three points, they are intended to define the curve, and hence should be widely spaced. Options include 1, 2 or 3.
Point spacing (ground)
Approximate distance between the points on the final catenary curve. (ground, default=1)
Line search radius (ground)
Search radius and endpoint extend distance when searching for lines to join or extend. (ground, default=10)
Local Commands
The following key-ins may be used to change run-time parameters. They may be keyed in, placed in macros or more commonly placed in the Local Args field in a Function Key.
Key-in |
Description |
Range |
Lay= |
Layer number |
1-32001 |
Mod= |
Mode |
1=Line 2=Spline |
Grp= |
Graphic pointer |
1-1000 |
Wid= |
Line width |
0-255 |
Pen= |
Pen number |
1-256 |
Con= |
Construction flag |
0-1 |
Ngr= |
Non graphic pointer |
32-bit |
Lnk= |
Link number |
32-bit |
Fc= |
Feature code |
15 char |
|
|
|
NumPts= |
Number user input points |
1-3 |
PntSpa= |
Point spacing |
ground (default=1) |
LinSea= |
Line search radius |
ground (default=10) |