Vr Mapping |
ON-LINE REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION CARDINAL SYSTEMS, LLC |
Shape Out (ShpOut)
Type: Translator
Translates VrOne file(s) to ArcView Shapefile format.
The Shapefile format is used by ArcView GIS software sold by Esri corporation. At the time of writing, a free Shapefile viewer named ArcExplorer is available for download at the Esri web site.
This description of the shapefile format is taken from Esri documentation:
"A shapefile stores non-topological geometry and attribute information for the spatial features in a data set. The geometry for a feature is stored as a shape comprising a set of vector coordinates. Because shapefiles do not have the processing overhead of a topological data structure, they have advantages over other data sources such as faster drawing speed and edit ability. Shapefiles handle single features that overlap or that are noncontiguous. They also typically require less disk space and are easier to read and write. Shapefiles can support point, line, and area features. Area features are represented as closed loop, double-digitized polygons. Attributes are held in a dBASE® format file. Each attribute record has a one-to-one relationship with the associated shape record."
A shapefile consists of one main file, one index file, and one dBASE table file. All file names adhere to the 8.3 naming convention. The main file, the index file, and the dBASE file have the same prefix. The prefix consists of an alphanumeric character (a–Z, 0–9) followed by up to seven characters (a–Z, 0–9, _, -). The suffix for the main file is .shp. The suffix for the index file is .shx. The suffix for the dBASE table is .dbf.
NOTE: The 8 character limit on filenames has been removed. ShpIn supports the longer filenames.
Example:
Main file: |
counties.shp |
Index file: |
counties.shx |
dBASE table: |
counties.dbf |
Shapefiles may only contain one feature per file. This means that points and lines must be translated into separate files. This also means that the file containing lines will either have all polylines or all polygons (closed areas), but not both. You can create up to four separate file types during one translation. Each file may have its postfix, contents, and dimension (2D or 3D) defined. Each VrOne layer can be translated into a separate set of theme files if needed. VrOne symbols are translated into the Point shapefile. VrOne lines are translated into the PolyLine and Polygon shapefile. VrOne text entities may be translated into a PolyLine file and represented as 2 point lines.
Example:
INPUT PARAMETERS
Shape base file name: |
bnd5533 |
Points postfix: |
pt |
Polylines postfix: |
ln |
Text lines postfix: |
tx |
OUTPUT FILES
bnd5533pt.shp
bnd5533pt.shx
bnd5533pt.dbf
bnd5533ln.shp
bnd5533ln.shx
bnd5533ln.dbf
bnd5533tx.shp
bnd5533tx.shx
bnd5533tx.dbf
The attributes assigned to entities in the shapefile may be customized using the cross-reference tables. The translator will try to assign default values so a quick translation can be accomplished without editing the cross-reference tables.
The user may define the field names and types used to hold entity attributes in the shapefile. The fields are taken from the following VrOne attributes: Layer, Graphic Pointer (Line Font/Symbol Name), Non-Graphic Pointer, and Feature Code.
Layer numbers, line font names, and symbol names from VrOne may be cross-referenced with attribute names in the shapefile.
NOTE: Only entities on layers contained in the Layer Cross-Reference table are considered for translation.
|
||
|
|
|
Shape Out
Loads a previously recorded Shape Out (.sho) parameter file.
Records current translation parameters to a Shape Out (.sho) parameter file.
Initializes translation parameters to default values. NOTE: Current translation parameters will be lost.
Allows editing general translation parameters.

General Tab
Translate each workspace into a separate shape file?
Specifies whether to write a separate shapefile for each open workspace. The shapefile filename prefixes are the same as the workspace filename. The theme postfixes are still be appended to each filename.
Translate each layer into a separate shape file?
Specifies whether to write a separate shapefile for each layer containing data. The shapefile filename prefixes are the same as the layer name. The theme postfixes will still be appended to each filename.
Shape base file name
Defines the base shapefile name to which to write translated data. The main shapefile, shapefile index, and shapefile dBASE files use this name with extensions of .shp, .shx, and .dbf, respectively. If any of the shape files exist, they are overwritten.
Workspaces to consider
Defines the workspaces to use when translating VrOne data to a shapefile. Options are “Current only” or “All open”.
Theme file 1-4 tabs
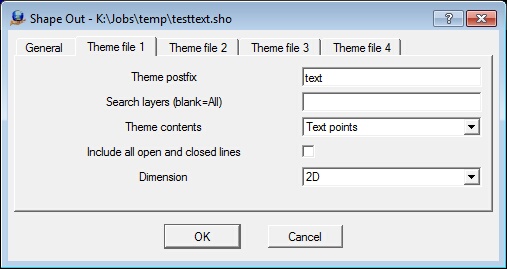
Theme postfix
Defines postfix to add to the Shape base file name when creating the shape file for this theme.
Search layers
Determines what layers are used for this theme. Should be entered as a number line. If left blank, all layers are considered.
Defines how lines are translated to the shapefile.
None |
This theme is not used. |
Points |
This theme contains points. VrOne symbols are written to this file. |
PolyLine |
This theme contains polylines. By default, only open lines are written to this file. NOTE: The “Include all open and closed lines” option overrides this. |
Polygon |
This theme contains polygons. By default, only closed lines will be written to this file. NOTE: The “Include all open and closed lines” option overrides this. In that case, open lines in VrOne have a segment added connecting their last and first points in the shapefile. |
Text Lines |
This theme contains two-point polylines representing text entities. Each VrOne text entity is translated as a two-point line passing horizontally through the center of the text label. |
Text Points |
This theme contains single points representing text entities. Each VrOne text entity is translated as a point. |
Include all open and closed lines
Determines if all lines are written or only those that match the content type if the theme contains polylines or polygons. For example, if the theme content is PolyLine, by default only open lines are written. If this box is checked, all closed lines are also written to the polylines file. On the other hand, if the content is polygons, by default only closed lines are written. If this box is checked, all open lines are also written to the polygons file.
Dimension
Determines the dimension to use for this theme. Options are:
2D |
2-dimension shape point file. |
3D |
3-dimension shape point file. |
NOTE: The free ArcExplorer shapefile viewer does not display elevations when viewing 3D files.
Edit Vr Feature Names
Allows editing feature name fields that correspond to VrOne entity attributes. Layer, Graphic Pointer (Line Font/Symbol Name), Non-Graphic Pointer, and Feature code attributes may all be mapped to feature attributes in the shapefile database. For instance, if the VrOne Layer attribute were mapped to a shapefile feature named "LAYER", the shapefile database would contain a LAYER field for each entity. This field would be filled with the value specified in the Layer cross-reference.
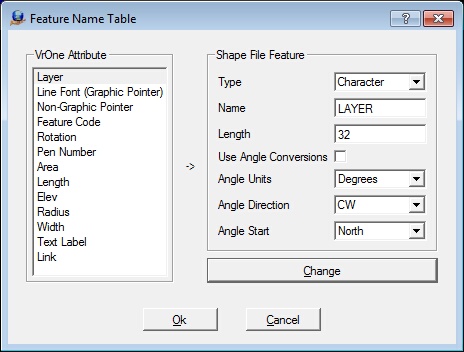
VrOne Attribute
Displays the VrOne attributes that can be cross-referenced with shapefile feature fields. Clicking an entry copies the settings to the Shape File Feature fields, where they may be changed. Always press the “Change” button after completing any edits.
Type
Defines the type of shapefile database field used for the selected VrOne attribute. Options are Numeric or Character.
Name
Defines the name of the shapefile database field used for the selected VrOne attribute. Any name longer than 10 characters is truncated.
Length
Defines the maximum length of the field. A maximum value of 19 is allowed for numeric fields, and 255 for character fields. Do not specify a larger length than needed, as this affects the size of the .dbf output file.
Use Angle Conversions
If this is on and the field type is Float, then the attribute will be treated as a rotation angle and converted according to the Angle settings below. If your viewer supports the display of symbols with rotations, then you may need to experiment with the angle conversion settings to get the correct settings to match the rotation of symbols in VrOne.
Angle Units
Defines the output units when converting attributes to angles. This can be Degrees or Radians. Only used if “Use Angle Conversions” is on.
Angle Direction
Defines the output angle direction when converting attributes to angles. This can be CW (clockwise) or CCW (counterclockwise). Only used if “Use Angle Conversions” is on.
Angle Start
Defines the output angle starting direction. This can be North, East, South, or West. Only used if “Use Angle Conversions” is on.
Defines the settings for cross-referencing VrOne layer numbers with attribute values in the shapefile database. The attribute field name for Layers is defined in the Edit Feature Names dialog.
The “Add Layers” option provides an easy way to define this table. This scans the current VrOne file(s) and creates a layer cross-reference entry for each layer used.
NOTE: If layer names have been defined in VrOne, they are used in the table. If a layer name has not been defined in VrOne, the layer number is used instead (with the word “Layer” before the number).
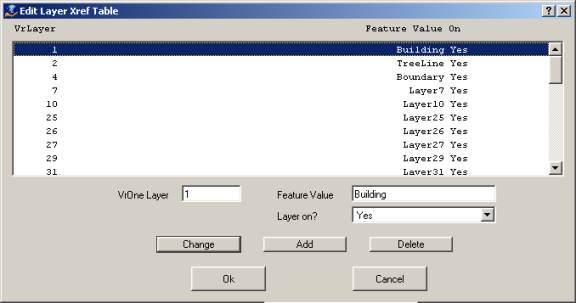
VrOne Layer
Specifies the VrOne input layer.
Feature Value
Defines value to put in the Layer feature field of the shapefile database.
Layer on
Specifies whether the current VrOne Layer is to be translated.
Defines the settings for cross-referencing VrOne line fonts with attribute values in the shapefile database. The attribute field name for Line Fonts (also known as Graphic Pointer) is defined in the Edit Feature Names dialog.
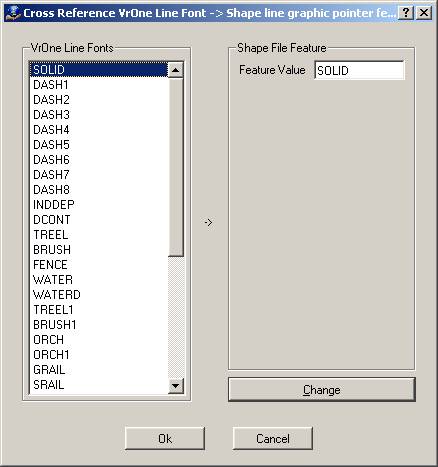
VrOne Line Fonts
Displays VrOne line font names for the current VrOne symbol file. Clicking an entry copies its settings to the Shape File Feature fields, where they may be changed.
Feature Value
Defines the value to place in the line font graphic pointer attribute field for each occurrence of this line font.
Defines the settings for cross-referencing VrOne symbols with attribute values in the shapefile database. The attribute field name for symbols is defined in the Edit Feature Names dialog.
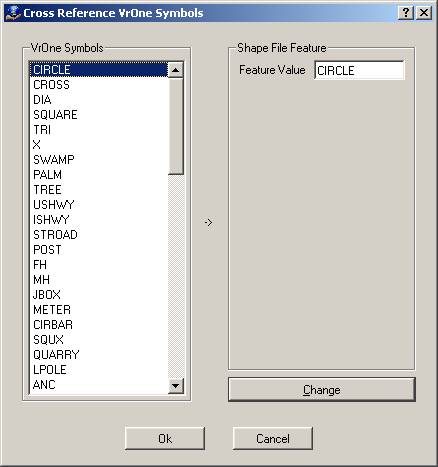
VrOne Symbols
Displays the VrOne line font names for the current VrOne symbol file. Clicking an entry will copy the settings to the Shape File Feature fields where they may be changed.
Feature Value
Defines the value to place in the symbol graphics pointer attribute field for each occurrence of this symbol.
Scans open VrOne file(s) and copies the layers used to the layer cross-reference table. “Cross-Reference Layers" may be used to cross-reference VrOne layer numbers to shapefile attribute values. If layer names have been defined in VrOne, those layer names are used in the table. If a layer name has not been defined in VrOne, the layer number will be used instead (with the word “Layer” before the number).
The following may be done to translate VrOne file(s) to a DXF file in the fewest possible steps. The result is a translation with all lines translated as solid, symbols translated as blocks, and text labels translated with the proper text font styles.
| 2. | Define the “Shape base file name” and the "Theme Postfix" setting for points and lines in “Edit Parameters”. |
| 4. | Translate. |